About Course
Introduction to Biodiversity
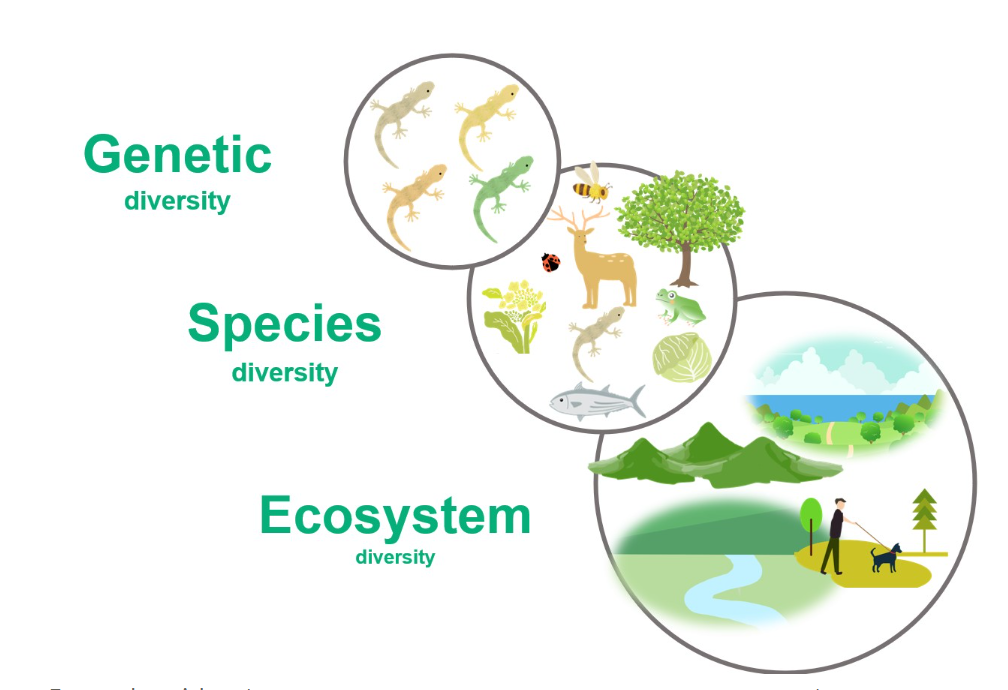
Biodiversity, short for biological diversity, refers to the variety and variability of life on Earth. It encompasses the diversity within species (genetic diversity), between species (species diversity), and among ecosystems (ecosystem diversity). This diversity is the foundation of life processes that sustain ecosystems and human societies.
Biodiversity ensures the stability and productivity of ecosystems by allowing organisms to adapt to changing environmental conditions. It supports vital ecological services such as pollination, nutrient cycling, climate regulation, and soil fertility. Moreover, it provides humans with food, medicine, raw materials, and cultural inspiration.
However, human activities such as deforestation, pollution, overexploitation, and climate change have greatly threatened biodiversity. Conservation of biodiversity is therefore essential for maintaining ecological balance and ensuring sustainable development for future generations.
Course Content
Meaning of key ecological terms and biodiversity
-
Key Ecological Terms and Biodiversity
identification of biodiversity
Importance of biodiversity
The threats and consequences of biodiversity loss
Student Ratings & Reviews

